How Does Mars Compare To Earth In Size?
At one time, astronomers believed the surface of Mars was crisscrossed by culvert systems. This in plow gave ascent to speculation that Mars was very much like Earth, capable of supporting life and dwelling to a native civilization. But as homo satellites and rovers began to bear flybys and surveys of the planet, this vision of Mars quickly dissolved, replaced by one in which the Red Planet was a common cold, desiccated and lifeless world.
However, over the past few decades, scientists have come to larn a bang-up deal about the history of Mars that has contradistinct this view likewise. We now know that though Mars may currently be very common cold, very dry, and very inhospitable, this wasn't ever the case. What's more, we have come to see that even in its current form, Mars and Globe actually take a lot in common.
Between the two planets, at that place are similarities in size, inclination, structure, composition, and even the presence of water on their surfaces. That existence said, they also have a lot of primal differences that would make living on Mars, a growing preoccupation among many humans (looking at y'all, Elon Musk and Bas Lansdorp!), a significant challenge. Permit'south get over these similarities and the divergence in an orderly fashion, shall we?
Sizes, Masses and Orbits:
In terms of their size and mass, Earth and Mars are quite different. With a mean radius of 6371 km and a mass of five.97×ten24 kg, World is the 5th largest and fifth nigh-massive planet in the Solar System, and the largest of the terrestrial planets. Mars, meanwhile, has a radius of approximately 3,396 km at its equator (3,376 km at its polar regions), which is the equivalent of roughly 0.53 Earths. Nonetheless, it's mass is just 6.4185 10 10²³ kg, which is effectually ten.vii% that of Globe'due south.

Similarly, Earth'south book is a hefty one.08321 x x12 km3, which works out one,083 billion cubic kilometers. By comparison, Mars has a volume of 1.6318 x 10¹¹ km³ (163 billion cubic kilometers) which is the equivalent of 0.151 Earths. Between this divergence in size, mass, and book, Mars's surface gravity is 3.711 m/s², which works out to 37.half-dozen% of Earths (0.376grand).
In terms of their orbits, Earth and Mars are likewise quite unlike. For instance, Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance (aka. semi-major axis) of 149,598,261 km – or one Astronomical Unit (AU). This orbit has a very minor eccentricity (approx. 0.0167), which means its orbit ranges from 147,095,000 km (0.983 AU) at perihelion to 151,930,000 km (1.015 AU) at aphelion.
At its greatest distance from the Sun (aphelion), Mars orbits at a distance of approximately 249,200,000 km (one.666 AU). At perihelion, when it is closest to the Sun, it orbits at a altitude of approximately 206,700,000 km (1.3814 AU). At these distances, the World has an orbital period of 365.25 days (1.000017 Julian years) while Mars has an orbital menstruum of 686.971 days (1.88 Earth years).
However, in terms of their sidereal rotation (time it takes for the planet to complete a unmarried rotation on its axis) World and Mars are once more in the same boat. While Earth takes precisely 23h 56m and 4 s to complete a unmarried sidereal rotation (0.997 World days), Mars does the same in about 24 hours and 40 minutes. This means that 1 Martian mean solar day (aka. Sol) is very close to unmarried solar day on Earth.

Mars's centric tilt is very similar to Earth's, existence inclined 25.19° to its orbital aeroplane (whereas Globe's axial tilt is but over 23°). This ways that Mars also experiences seasons and temperature variations like to that of Earth (run across beneath).
Structure and Composition:
Earth and Mars are similar when it comes to their bones makeups, given that they are both terrestrial planets. This means that both are differentiated between a dense metal core and an overlying pall and crust composed of less dense materials (like silicate rock). Notwithstanding, World's density is college than that of Mars – 5.514 g/cm3 compared to 3.93 g/cm³ (or 0.71 Earths) – which indicates that Mars' core region contains more than lighter elements than Earth's.
Earth's core region is made up of a solid inner core that has a radius of virtually 1,220 km and a liquid outer cadre that extends to a radius of most 3,400 km. Both the inner and outer cores are equanimous of iron and nickel, with trace amounts of lighter elements, and together, they add to a radius that is every bit big as Mars itself. Current models of Mars' interior advise that its core region is roughly 1,794 ± 65 kilometers (ane,115 ± 40 mi) in radius, and is composed primarily of iron and nickel with about xvi-17% sulfur.
Both planets take a silicate pall surrounding their cores and a surface crust of solid fabric. Earth'due south drapery – consisting of an upper mantle of slightly viscous material and a lower drapery that is more solid – is roughly 2,890 km (1,790 mi) thick and is equanimous of silicate rocks that are rich in iron and magnesium. The Earth'south chaff is on average xl km (25 mi) thick, and is composed of rocks that are rich in iron and magnesium (i.e. igneous rocks) and granite (rich in sodium, potassium, and aluminum).

Insufficiently, Mars' mantle is quite thin, measuring some 1,300 to ane,800 kilometers (800 – 1,100 mi) in thickness. Like World, this drape is believed to be composed of silicate rock that are rich in minerals compared to the crust, and to be partially viscous (resulting in convection currents which shaped the surface). The chaff, meanwhile, averages about 50 km (31 mi) in thickness, with a maximum of 125 km (78 mi). This makes it about iii times every bit hick equally Globe's crust, relative to the sizes of the two planets.
Ergo, the two planets are similar in composition, owing to their common status every bit terrestrial planets. And while they are both differentiated between a metallic core and layers of less dense fabric, there is some variance in terms of how proportionately thick their respective layers are.
Surface Features:
When it comes to the surfaces of Globe and Mars, things once once more become a case of contrasts. Naturally, it is the differences that are most apparent when comparing Blue World to the Scarlet Planet – as the nicknames would advise. Dissimilar other planet's in our Solar Arrangement, the vast majority of Earth is covered in liquid water, most lxx% of the surface – or 361.132 1000000 km² (139.43 million sq mi) to be exact.
The surface of Mars is dry, dusty, and covered in dirt that is rich iron oxide (aka. rust, leading to its reddish appearance). However, large concentrations of ice water are known to exist inside the polar water ice caps – Planum Boreum and Planum Australe. In addition, a permafrost mantle stretches from the pole to latitudes of about 60°, significant that ice water exists beneath much of the Martian surface. Radar data and soil samples have confirmed the presence of shallow subsurface water at the middle latitudes as well.
As for the similarities, Earth and Mars' both have terrains that varies considerably from place to place. On Earth, both higher up and below sea level, there are mountainous features, volcanoes, scarps (trenches), canyons, plateaus, and abyssal plains. The remaining portions of the surface are covered by mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, and other landforms.
Mars is quite like, with a surface covered by mountain ranges, sandy plains, and even some of the largest sand dunes in the Solar Arrangement. It also has the largest mountain in the Solar System, the shield volcano Olympus Mons, and the longest, deepest chasm in the Solar System: Valles Marineris.
Earth and Mars take besides experienced many impacts from asteroids and meteors over the years. However, Mars' own impact craters are far better preserved, with many dating back billions of years. The reason for this is the depression air pressure and lack of precipitation on Mars, which results in a very slow rate of erosion. Even so, this was not always the case.
Mars has discernible gullies and channels on its surface, and many scientists believe that liquid water used to menstruum through them. By comparing them to similar features on Globe, it is believed that these were were at least partially formed by h2o erosion. Some of these channels are quite large, reaching 2,000 kilometers in length and 100 kilometers in width.
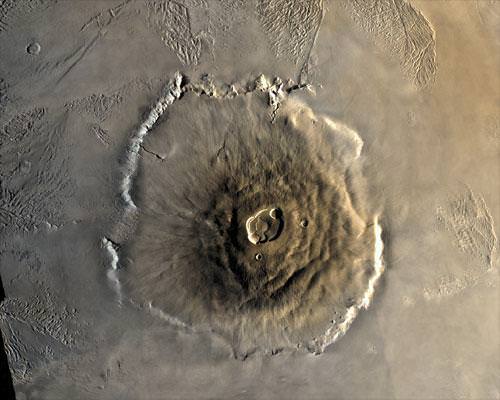
So while they wait quite dissimilar today, Earth and Mars were once quite like. And similar geological processes occurred on both planets to give them the kind of varied terrain they both currently have.
Atmosphere and Temperature:
Atmospheric pressure and temperatures are another mode in which World and Mars are quite different. World has a dense atmosphere composed of five principal layers – the Troposphere, the Stratosphere, the Mesosphere, the Thermosphere, and the Exosphere. Mars' is very thin by comparison, with pressure level ranging from 0.4 – 0.87 kPa – which is equivalent to well-nigh 1% of Earth's at sea level.
World'due south temper is also primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) with trace concentrations of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other gaseous molecules. Mars' is equanimous of 96% carbon dioxide, 1.93% argon and 1.89% nitrogen along with traces of oxygen and h2o. Contempo surveys have also noted trace amounts of methane, with an estimated concentration of about 30 parts per billion (ppb).
Because of this, in that location is a considerable difference between the average surface temperature on Earth and Mars. On Earth, it is approximately 14°C, with enough of variation due to geographical region, height, and time of year. The hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 70.vii°C (159°F) in the Lut Desert of Iran, while the coldest temperature was -89.2°C (-129°F) at the Soviet Vostok Station on the Antarctic Plateau.
![Space Shuttle Endeavour sillouetted against the atmosphere. The orange layer is the troposphere, the white layer is the stratosphere and the blue layer the mesosphere.[1] (The shuttle is actually orbiting at an altitude of more than 320 km (200 mi), far above all three layers.) Credit: NASA](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/Endeavour_silhouette_STS-130-580x387.jpg)
Because of its thin atmosphere and its greater altitude from the Sun, the surface temperature of Mars is much colder, averaging at -46 °C (-51 °F). However, because of its tilted axis and orbital eccentricity, Mars also experiences considerable variations in temperature. These can be seen in the form of a low temperature of -143 °C (-225.four °F) during the winter at the poles, and a high of 35 °C (95 °F) during summer and midday at the equator.
The temper of Mars is also quite dusty, containing particulates that measure 1.5 micrometers in diameter, which is what gives the Martian sky a tawny color when seen from the surface. The planet also experiences grit storms, which tin can turn into what resembles small tornadoes. Larger dust storms occur when the dust is blown into the temper and heats up from the Sun.
And then basically, Globe has a dense temper that is rich in oxygen and water vapor, and which is mostly warm and conducive to life. Mars, meanwhile, is by and large very cold, but can become quite warm at times. It'due south also quite dry and very dusty.
Magnetic Fields:
When information technology comes to magnetic fields, Earth and Mars are in stark contrast to each other. On Earth, the dynamo event created by the rotation of World's inner core, relative to the rotation of the planet, generates the currents which are presumed to be the source of its magnetic field. The presence of this field is of extreme importance to both World'due south atmosphere and to life on Globe as we know it.
Substantially, Earth's magnetosphere serves to deflect most of the solar air current'due south charged particles which would otherwise strip abroad the ozone layer and expose Earth to harmful radiation. The field ranges in forcefulness betwixt approximately 25,000 and 65,000 nanoteslas (nT), or 0.25–0.65 Gauss units (G).
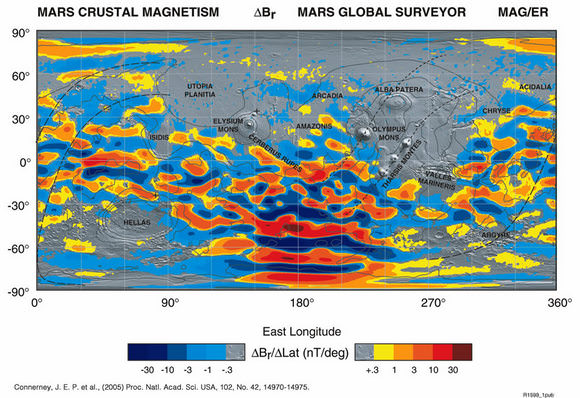
Today, Mars has weak magnetic fields in various regions of the planet which appear to be the remnant of a magnetosphere. These fields were first measured by the Mars Global Surveyor, which indicated fields of inconsistent strengths measuring at almost 1500 nT (~16-xl times less than Earth'southward). In the northern lowlands, deep impact basins, and the Tharsis volcanic province, the field strength is very low. But in the ancient southern crust, which is undisturbed by giant impacts and volcanism, the field forcefulness is higher.
This would seem to bespeak that Mars had a magnetosphere in the past, and explanations vary as to how information technology lost it. Some suggest that it was blown off, along with the majority of Mars' atmosphere, by a big impact during the Late Heavy Bombardment. This impact, information technology is reasoned, would have also upset the estrus flow in Mars' iron core, arresting the dynamo effect that would have produced the magnetic field.
Some other theory, based on NASA'due south MAVEN mission to study the Martian atmosphere, has it that Mars' lost its magnetosphere when the smaller planet cooled, causing its dynamo effect to terminate some 4.ii billion years ago. During the next several hundred million years, the Lord's day'due south powerful solar current of air stripped particles away from the unprotected Martian atmosphere at a rate 100 to 1,000 times greater than that of today. This in turn is what caused Mars to lose the liquid water that existed on its surface, as the environment to become increasing common cold, desiccated, and inhospitable.
Satellites:
Earth and Mars are also similar in that both have satellites that orbit them. In Earth'southward case, this is none other than The Moon, our only natural satellite and the source of the World's tides. It'south existence has been known of since prehistoric times, and it has played a major role in the mythological and astronomical traditions of all human cultures. In addition, its size, mass and other characteristics are used as a reference indicate when assessing other satellites.
The Moon is one of the largest natural satellites in the Solar System and is the 2d-densest satellite of those whose moons who'southward densities are known (after Jupiter'south satellite Io). Its bore, at iii,474.8 km, is one-fourth the diameter of Earth; and at 7.3477 × 1022 kg, its mass is 1.ii% of the World's mass. Information technology's mean density is iii.3464 g/cm3 , which is equivalent to roughly 0.half dozen that of Earth. All of this results in our Moon possessing gravity that is about xvi.54% the strength of World's (aka. 1.62 m/s2 ).
The Moon varies in orbit around Earth, going from 362,600 km at perigee to 405,400 km at apogee. And similar most known satellites within our Solar System, the Moon'due south sidereal rotation catamenia (27.32 days) is the same equally its orbital period. This ways that the Moon is tidally locked with Earth, with one side is constantly facing towards usa while the other is facing abroad.
Cheers to examinations of Moon rocks that were brought back to World, the predominant theory states that the Moon was created roughly 4.5 billion years ago from a standoff between Earth and a Mars-sized object (known every bit Theia). This collision created a massive cloud of debris that began circling our planet, which eventually coalesced to form the Moon we see today.
Mars has ii small satellites, Phobos and Deimos. These moons were discovered in 1877 by the astronomer Asaph Hall and were named after mythological characters. In keeping with the tradition of deriving names from classical mythology, Phobos and Deimos are the sons of Ares – the Greek god of war that inspired the Roman god Mars. Phobos represents fright while Deimos stands for terror or dread.
Phobos measures nearly 22 km (14 mi) in bore, and orbits Mars at a distance of ix,234.42 km when it is at periapsis (closest to Mars) and ix,517.58 km when it is at apoapsis (uttermost). At this distance, Phobos is below synchronous altitude, which means that information technology takes simply 7 hours to orbit Mars and is gradually getting closer to the planet. Scientists guess that in 10 to 50 million years, Phobos could crash into Mars' surface or interruption up into a band structure around the planet.
Meanwhile, Deimos measures about 12 km (seven.5 mi) and orbits the planet at a distance of 23,455.v km (periapsis) and 23,470.ix km (apoapsis). It has a longer orbital period, taking 1.26 days to complete a full rotation around the planet. Mars may have additional moons that are smaller than 50- 100 meters (160 to 330 ft) in bore, and a dust ring is predicted betwixt Phobos and Deimos.
Scientists believe that these two satellites were once asteroids that were captured by the planet's gravity. The low albedo and the carboncaceous chondrite composition of both moons – which is similar to asteroids – supports this theory, and Phobos' unstable orbit would seem to suggest a recent capture. However, both moons accept circular orbits nearly the equator, which is unusual for captured bodies.
Then while Earth has a unmarried satellite that is quite large and dumbo, Mars has two satellites that are minor and orbit it at a comparatively shut distance. And whereas the Moon was formed from World'due south own debris after a rather severe collision, Mars' satellites were likely captured asteroids.
Conclusion:
Okay, permit's review. Globe and Mars have their share of similarities, merely besides some rather stark differences.
Mean Radius: 6,371 km 3,396 km
Mass: 59.vii×1023 kg 6.42 x x²³ kg
Volume: 10.eight x 1011 km3 1.63 x 10¹¹ km³
Semi-Major Centrality: 0.983 – ane.015 AU one.3814 – 1.666 AU
Air Force per unit area: 101.325 kPa 0.4 – 0.87 kPa
Gravity:9.8 1000/s² 3.711 m/south²
Avg. Temperature: 14°C (57.2 °F) -46 °C (-51 °F)
Temp. Variations: ±160 °C (278°F) ±178 °C (320°F)
Centric Tilt: 23° 25.19°
Length of Twenty-four hours: 24 hours 24h 40m
Length of Yr: 365.25 days 686.971 days
H2o: Plentiful Intermittent (generally frozen)
Polar Ice Caps: Yep Yep
In short, compared to Earth, Mars is a pretty small, dry, cold, and dusty planet. It has comparatively low gravity, very niggling temper and no breathable air. And the years are also mighty long, almost twice that of Earth, in fact. Still, the planet does accept its fair share of water (albeit generally in water ice form), has seasonal cycles similar to Earth, temperature variations that are similar, and a day that is about every bit long.
All of these factors will accept to exist addressed if ever human being beings want to live there. And whereas some can be worked with, others volition accept to be overcome or adjusted to. And for that, nosotros volition have to lean pretty heavily on our technology (i.e. terraforming and geoengineering). Best of luck to those who would like to venture there anytime, and who practise not plan on coming home!
We have written many articles nigh Mars here on Universe Today. Here's an article most how difficult it volition be to land large payloads onto the surface of Mars, and here's an article almost the Mars methane mystery.
And hither are some on the altitude between Earth and Mars, Mars' gravity, and if humans can live on Mars.
If y'all'd like more than info on Mars, check out Hubblesite's News Releases about Mars, and hither's a link to the NASA Mars Exploration home page.
And be sure to bank check out NASA'south Solar Arrangement Exploration: Earth and Mars Comparing Chart
Nosotros have recorded several podcasts just about Mars. Including Episode 52: Mars and Episode 92: Missions to Mars, Office 1.
Sources:
- NASA – All About Mars
- NASA: Solar Organization Overview – World
- University of Phoenix – Mars Mission
- Wikipedia – Mars
How Does Mars Compare To Earth In Size?,
Source: https://www.universetoday.com/22603/mars-compared-to-earth/
Posted by: skeltonsonters.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Does Mars Compare To Earth In Size?"
Post a Comment